Alerting on Network Traffic Anomalies with ntopng
Today I’d like to tell you about the possibility of alerting when anomalies in network traffic are encountered.
I use ntopng to generate, evaluate and forward these alerts. If you don’t know about ntopng, let me briefly describe for you what it does.
According to its creator, ntopng is a High-Speed Web-based Traffic Analysis and Flow Collection tool. ntopng is a network traffic probe that provides 360° network visibility, with its ability to gather traffic information from traffic mirrors, Netflow exporters, SNMP devices, firewall logs, and intrusion detection systems.
ntopng provides an intuitive (and encrypted) web user interface for the exploration of both real time and historical traffic information.
It also offers a number of predefined alarms in the following areas, which can be activated and their thresholds adjusted as required:
- Active Monitoring: An active monitoring alerting system (e.g., host unreachable).
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Checks that evaluate the behavior of hosts and add them to the jailed hosts pool when deemed to be – suspicious. When ntopng is used in combination with nProbe IPS, suspicious hosts are blocked and prevented from generating traffic.
- Internals: Internal functionalities of ntopng (e.g., memory management, and host and flows lifecycles)
- Network: Network behaviors and anomalies (e.g., traffic above a certain threshold, TCP not working as expected)
- Other: Default category for uncategorized scripts or for those that cannot be included in any of the other categories
- Cybersecurity: Security behaviors and anomalies (e.g., contacts to or from a blacklisted host, TCP and UDP scans)
- SNMP: SNMP device status (e.g., Interface duplex status changes, SNMP device restart)
- System: Functionalities of the system on top of which ntopng is running (e.g, disk space full, load too high)
The currently set alarms can be evaluated under the alert view:
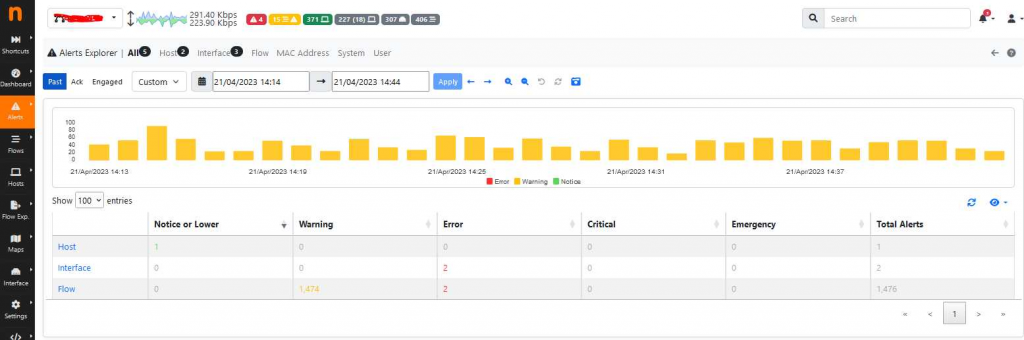
Any alarms raised can be Acknowledged, or placed on an exclude list if the alarms are not relevant to your environment:
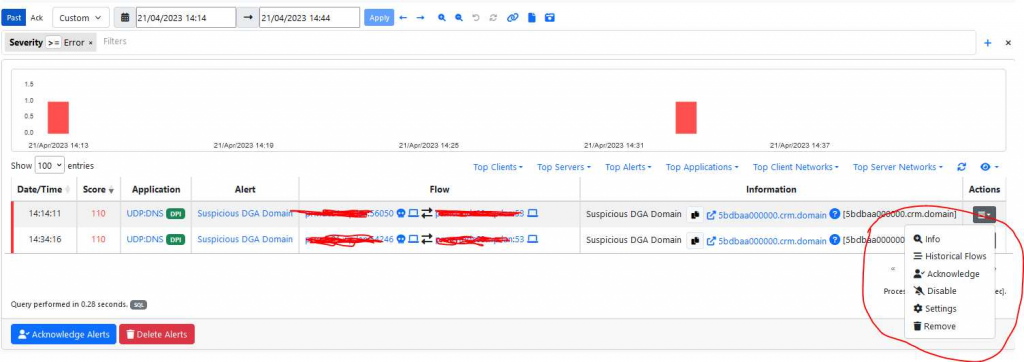
Alarms that are on the exclude list can be managed in the following interface and potentially reactivated:
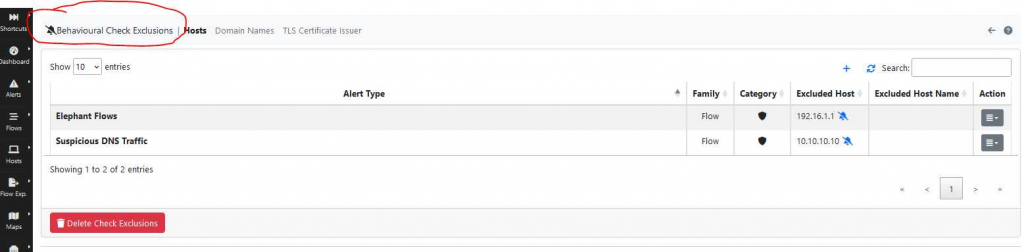
The threshold values can be adjusted in the “Behavioural Checks” interface:
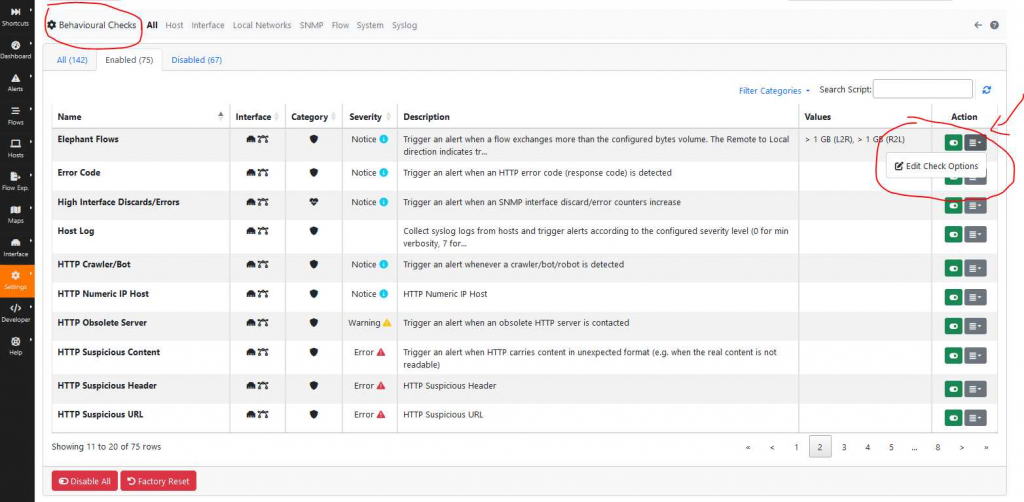
Triggered alarms can be sent to various endpoints such as email, MS Teams, Webhook, Telegram, Elasticsearch, etc., where they can be redirected.
Finally, I can report from experience that the use of ntopng can be used to detect anomalies for SIEM and SOC systems. The flows are analyzed via ntopng, anomalies are recognized based on rules, and are then forwarded to the SIEM or SOC system. This allows the targeted alarms to be processed and correlated in the SIEM and SOC system without overloading these systems with vast amounts of network flows.
These Solutions are Engineered by Humans
Did you read this article because you’re knowledgeable about networking? Do you have the skills necessary to manage networks? We’re currently hiring for roles like this as well as other roles here at Würth Phoenix.







