IT Orchestration in NetEye: Enable locked user account from Action Launchpad
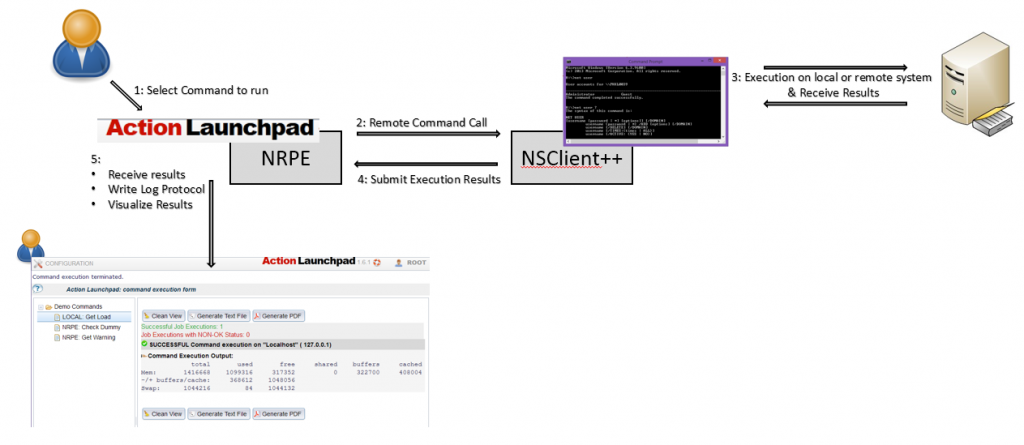
The IT Orchestration module ( also known as Action Launchpad ) comes with the purpose to simplify IT service operations. Operations can be configured within command calls that can be granted to users of your Service Operations Center. The module Action Launchpad allows to define command configurations to be called on request and job schedule on a remote server.
The advantage:
- Define an operation to perform once and call it easily with a simple click
- Avoid users to access remote systems for command call
- Grant permissions to dedicated users for specific commands
- Track the results
- Automate the execution with a build in scheduler
How does it work ?
Example of frequent operation: Enable a user Account
Repetitive tasks cost a lot of time to an IT operator and in the same moment can be even not be completely automated or outsourced. A necessity like this could be the call from a user “I can not login”, and the task to unlock the account or reset the password are a frequent consequence.
With this blog I would like to give an instruction how to integrate this task into an operation that could be performed with a simple click in NetEye.
1. Define the System Command to run
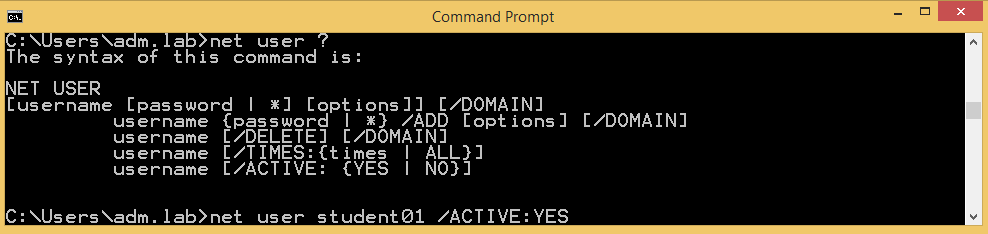
The next CMD shows the System Command call syntax to execute for resetting a user password. This structure should be saved as predefined call on this Windows host and being called from the NetEye Action Launchpad:
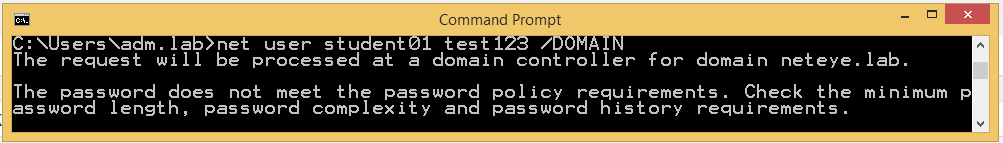
Reset user password: : This instruction defines the name of the user account for which to set the new password “test123”. Note, that the output we see here, is passed directly back to NetEye and shown later in the output dialog:
In order to create a simple structure to be called easily in a later moment I define a simple script file. This could be done with a .bat file, or on modern platforms we could adopt also the PowerShell instruction “Set-ADAccountPassword”. For this example I would use the “net user” instruction as this version will work on any Microsoft release.
The script is stored as domain_operations.bat into the “scripts” folder of the NetEyeNSClient++ installation folder (i.e. C:\Program Files\NetEyeNSClient++\scripts\ ).
2. Get the NSClient++ ready
We define the created script ( Download example: domain_operations.zip ) as a new command in the nsclient.ini within the section “settings/external scripts/scripts”. Next to this it is important to enable the arguments as we desire to pass the username and possible new password as parameter. In the same moment security should be condidered too: Limit the access to the NSClient++ service to the only IP address of the NetEye server. ( “allowed_hosts” instruction )
Section beeing added/adapted in nsclient.ini:
[/settings/external scripts]
; COMMAND ARGUMENT PROCESSING – This option determines whether or not the we will allow clients to specify arguments to commands that are executed.
allow arguments = 1
; COMMAND ALLOW NASTY META CHARS – This option determines whether or not the we will allow clients to specify nasty (as in |`&><‘”\[]{}) characters in arguments.
allow nasty characters = 1[/settings/external scripts/scripts]
; Some more commands
domain_operations=scripts\domain_operations.bat $ARG1$ $ARG2$ $ARG3$
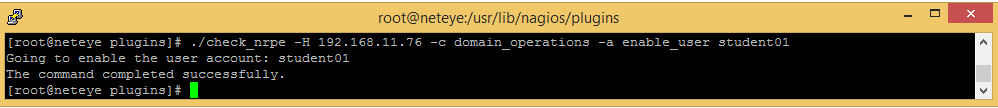
Now restart the service and test the command call by running the command from SSH:
ADVICE: The NSClient++ runs at “service” level. This might be not enough to access Domain ressources and it might be required to run the service as different user specifying the “Log on” tab.
3. Action Launchpad command definition
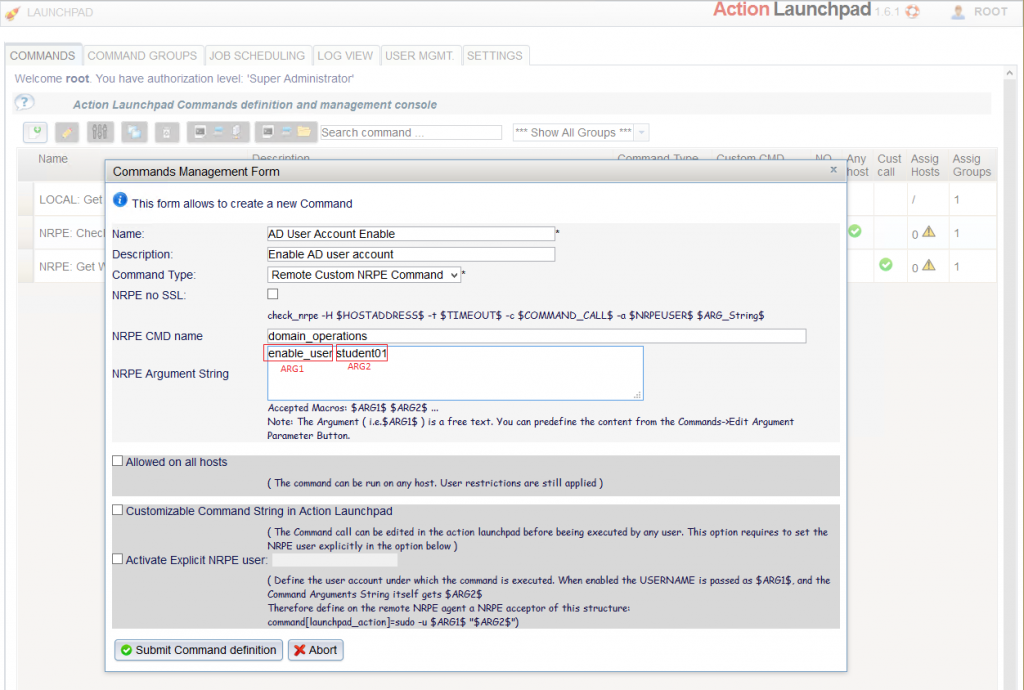
If you are able to run the desired command all via check_nrpe command you are ready to define your command in Action Launchpad. Therefore access with Admin rights the configuration console, tab: “Commands”. The Command definition holds the command name “domain_operations” and we choose therefore command type “Remote Custom NRPE Command”.
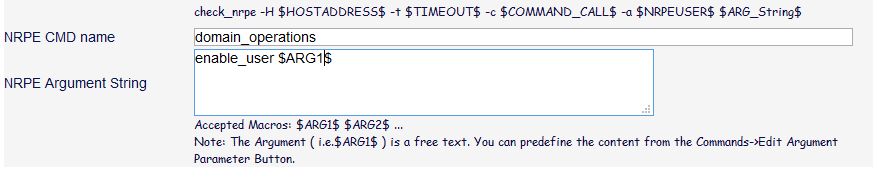
In the previous command definition we “hard coded” the argument, this means it is not possible to change the values on run time with a normal user account. But this feature is provided in Action Launchpad and it is even possible to define the available values in form of a drop-down box.
So change the value of the username to “$ARG1$”:
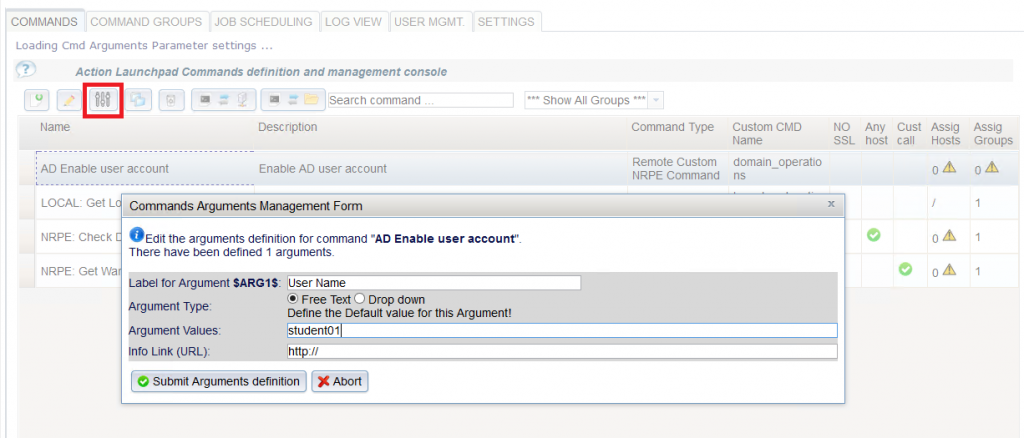
and specify a label for Argument 1 and also a value suggestion example:
- Now we define a Specific command group called “AD Account Operations” and Assign this command to the group.
- Enable the user accounts on that group in order to grant access to authorized users only.
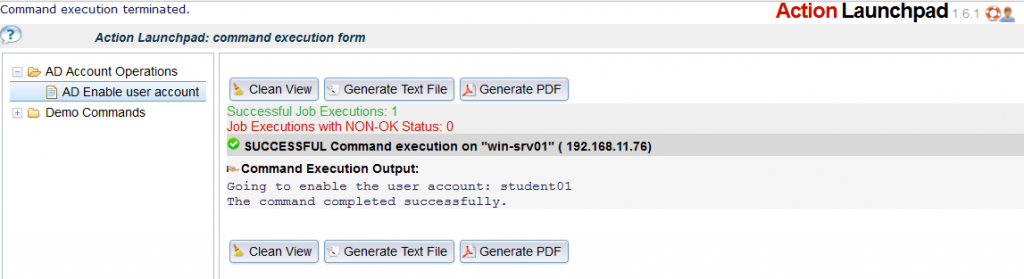
4. Perform Command Execution
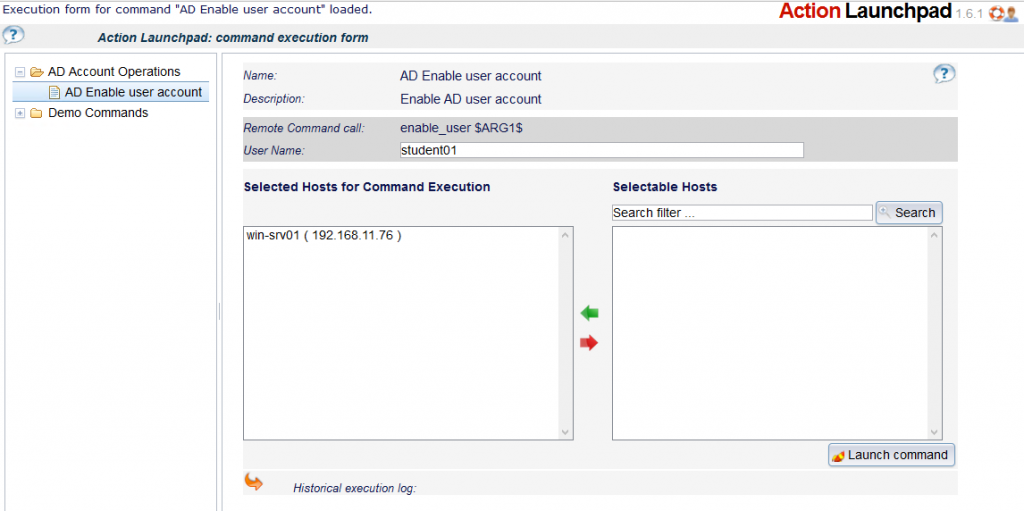
Login with an authorized user to the Action Launchpad:
- identify the Command to run
- fill in the desired user account to unlock ( we see the suggested ‘student01’ )
- Choose the host to run the command on ( The UI will remember the last selections )
- Perform the command execution:
The output of the command is shown once completed:
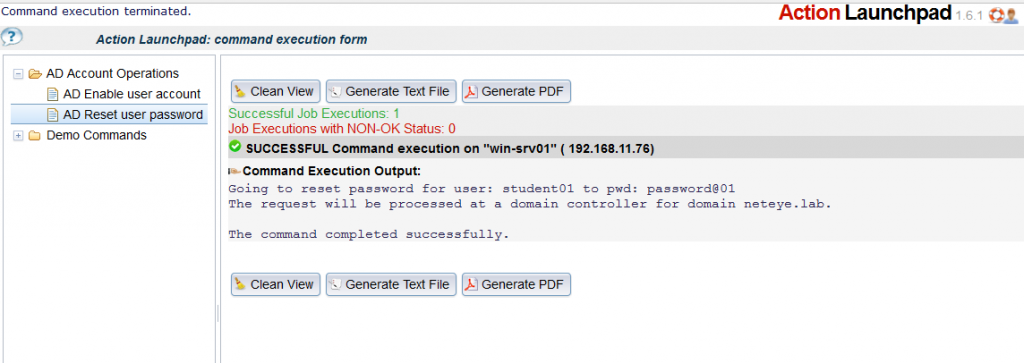
Example of Password reset:
Download: domain_operations.zip